No.2 new District Minglun Village,Wuxiang Town,Yinzhou District
-

Tel: +86 18658447778
-

E-mail: [email protected]
-
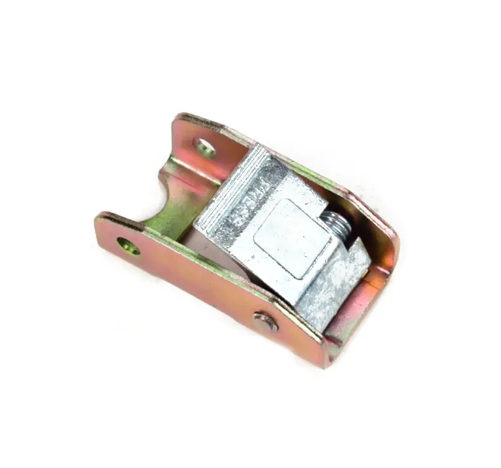

Alloy cam buckles (also called alloy buckles or clips) are common tools used to secure goods. They are widely used in transportation, handling, and storage, especially in trucks, containers, and logistics, to prevent goods from shifting during transport. Due to their robust structure, ease of operation, and strong securing ability, alloy cam buckles are widely used for cargo binding and securing.
Alloy Cam Buckles: Ensure the cam buckles are the correct model and specifications, capable of withstanding the required tension and weight.
Securing Straps/Straps (e.g., buckle straps or nylon straps): Straps are usually needed to secure the goods with alloy cam buckles.
Goods and Transport Vehicles: Such as containers, trucks, transport trucks, etc. Ensure the securing positions of the transport vehicles are prepared.
Strap Type: Select the appropriate straps based on the type of goods and transportation requirements. Generally, straps used may be nylon straps, polyester straps (PE straps), etc., as these materials are wear-resistant, tensile-resistant, and durable. Strap Width and Strength: Ensure the strap width and strength are suitable for the transported goods. If the goods are heavy, choose straps with stronger load-bearing capacity.
Securing One End of the Cam Buckle: Hook one end of the alloy cam buckle (usually the hook part) onto the fixed position of the goods, or find a fixing point on the side wall of the truck or the frame of the container. Ensure the hook is secure and not loose.
Passing the Strap: Pass one end of the strap through the main buckle slot of the alloy cam buckle (some alloy cam buckles may have multiple slots). Then wrap the strap around the goods, ensuring the strap does not slip or loosen.
Tightening the Strap: After wrapping the strap around the goods, use the **cam locking mechanism** of the alloy cam buckle to tighten the strap. The cam design of the cam buckle helps to tighten the strap and secure it through the locking mechanism. At this time, be careful to ensure that the strap does not slip and maintain sufficient tension.
Unlocking the Cam Lock: The alloy cam buckle usually has a rotatable cam. By rotating the cam, the strap can be further tightened. When tightening, apply force evenly to ensure the goods are not damaged by excessive pressure.
Locking the buckle: After tightening, rotate the cam or press the release lever to lock it into place. The cam buckle will then secure the straps and keep the goods firmly in place.
Check the strap tightness: Ensure the straps are fully tightened and not loose. If the straps show signs of loosening or slipping, readjust and tighten them.
Ensuring the goods are securely fixed: Gently push and pull the goods to confirm they are firmly secured and will not shift during transport. If the goods wobble or slip, the straps may need to be readjusted.
During transport, especially long-distance transport, it is recommended to regularly check the securing of the goods to ensure the alloy cam buckle and straps are not loose or damaged. Stops can be made en route for inspection, and the straps can be readjusted or replaced if necessary.
Clean Surface: After each use, promptly clean dust, dirt, oil stains, and other contaminants from the alloy cam buckle. Use a soft cloth or brush to gently wipe, avoiding scratches from hard materials.
Prevent Corrosion: The alloy cam buckle is prone to rust or corrosion if exposed to humid environments for extended periods. Pay special attention to cleaning to prevent rust, especially when used in marine environments, humid conditions, or chemical storage. Apply **rust-preventive oil** or a suitable metal surface protectant to protect the metal from corrosion.
Check for Loose or Damaged Buckles: Regularly inspect the cam locking device, latch, springs, and other components of the alloy cam buckle for damage. Sometimes, springs may fatigue due to frequent use, or the cam buckle locking mechanism may wear out. Ensure all components lock and unlock smoothly during operation.
Inspect Springs and Snap Rings: The springs in the cam buckle are typically used to provide sufficient locking force. Replace springs if they are rusty, broken, or loose. Ensure the snap rings close properly and do not loosen.
Check the strap connection point: The part where the alloy cam buckle connects to the strap is the most easily worn part during use. Regularly check the strap for wear or breakage, ensuring that the strap is not damaged due to excessive pressure or friction. If the strap is worn or broken, replace it with a new one immediately.
Check the buckle connection point: Confirm that the connection between the buckle and the strap is not loose or damaged to avoid safety hazards during transportation.
Avoid overloading: Each alloy cam buckle has its maximum load capacity and usage limits. Ensure that the rated load is not exceeded during use, otherwise it may cause damage or deformation of the alloy cam buckle. Overloading will not only affect the lifespan of the equipment but may also cause safety problems during transportation.
Use properly: If the alloy cam buckle has been used for a period of time and has undergone a lot of transportation work, it is recommended to check it and replace it in advance if necessary.
Avoid prolonged exposure to humid environments: Alloy cam buckles are prone to rust when exposed to high humidity environments for a long time, especially in humid environments such as maritime transport and heavy industry, where the risk of corrosion increases. Keep it away from water sources, moisture, salt spray, and other corrosive environments during use.
Avoid high temperatures or chemical contact: Avoid exposing the alloy cam buckle to high temperatures, excessive heat, or strong corrosive chemicals, as this may cause damage or deformation of the metal.